Southern nymphal deer ticks in hiding?
Researchers have identified adult blacklegged (Ixodes scapularis) ticks in the southern United States, specifically looking in Texas. Using the collection method of flagging and dragging, investigators found 656 adult ticks between October and April. But nymphal ticks were nowhere to be found.
Lyme disease mimics prosthetic joint infection following knee replacement
Lyme disease symptoms can mimic periprosthetic joint infection (PJI), which is caused by typical bacterial organisms. In their article “Lyme Disease: A Potential Source for Culture-negative Prosthetic Joint Infection,” Collins and colleagues describe the case of an elderly man who underwent surgery to treat what doctors initially believed was an infection of his prosthetic knee. [1]
Delayed onset of Babesia highlights importance of follow-up visits
A recent case report published in the British Medical Journal demonstrates the importance of monitoring patients with Lyme disease even after initial treatment, as co-infections can surface at a later stage.
Don’t be misled: patients can have both mono and Lyme disease
Mononucleosis (EBV) and Lyme disease share similar characteristics, making an accurate diagnosis difficult. Each condition causes non-specific symptoms including fatigue, fever, myalgia, arthritis, headaches, neck soreness and swollen or enlarged lymph nodes. And each greatly impacts children. While mono is a common childhood illness, 25% of all Lyme disease cases in the US involve children.
Infected ticks prevalent in urban areas in the United Kingdom (UK)
The prevalence of vector-borne diseases in Europe, including the UK, has changed dramatically over the past 15 years. Today, there are regular outbreaks of West Nile, chikungunya, and dengue viruses. Malaria has returned. The number of Lyme disease cases is rising and tick-borne encephalitis virus is expanding to the northern regions of Europe. Meanwhile, new pathogens continue to be discovered, such as Borrelia miyamotoi and various tick-borne rickettsiae.
First-line combination therapy for tick-borne illnesses
Black-legged ticks can carry and transmit multiple pathogens causing a range of different diseases including Lyme disease, Babesia, anaplasmosis, Borrelia miyamotoi, ehrlichiosis and the Powassan virus. In fact, an individual can develop several diseases from just a single tick bite.
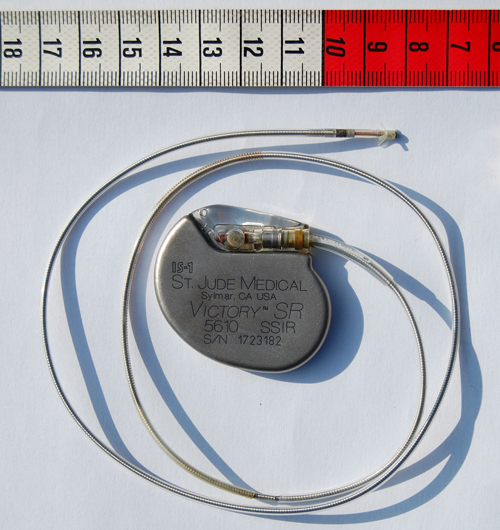
Can we avoid using a pacemaker for Lyme carditis with high-degree AV block?
A pacemaker implantation is typically an effective treatment for patients with high-degree atrioventricular (AV) block due to Lyme carditis (LC). “However, the AV block in LC may revert back to normal conduction and usually resolves within the first 10 days of antibiotic administration,” says Yeung from Queen’s University in Kingston, Ontario. [1] “If the AV block in LC is indeed transient, then a permanent pacemaker is not indicated.”
10 cases of Heartland virus reviewed
This past week, Illinois health officials reported the first case of Heartland virus in their state.
The disease, believed to be spread by the lone star tick, is relatively new. Although it was first identified in 2009 in Missouri, it wasn’t described in the medical literature until 2012, when researchers from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) announced that the virus could be “a more common cause of human illness than is currently recognized.” [1]
Lyme disease remains a threat to international travelers to the US
Researchers have primarily studied travel-related illnesses in individuals travelling from high-income countries (such as the United States) to low- and middle-income countries. But now as vector-borne diseases, including Lyme disease, become a growing threat in the USA, researchers are switching their attention to the dangers now faced by travelers visiting the States.
Citizen scientists help uncover growing risk of Babesia
Tick-borne pathogens have expanded into new geographical territories across the United States resulting in a greater incidence of tick-related diseases. Gathering data to understand patterns of exposure to tick bites and the risk of disease on a national level is becoming increasingly important. As a result, researchers have teamed up with citizen scientists (members of the public) to help collect samples and data.